
Ways to Reverse Type 2 Diabetes Naturally
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction to Type 2 Diabetes
As someone who has personally experienced the challenges of managing type 2 diabetes, I understand the importance of finding natural ways to reverse this condition. Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by high blood sugar levels caused by insulin resistance. It is often linked to lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity. In this article, I will share 10 effective strategies to help you reverse type 2 diabetes naturally and regain control of your health.
Understanding the Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
To effectively reverse type 2 diabetes, it is crucial to understand the underlying causes of the condition. In most cases, type 2 diabetes is a result of insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin. This can be triggered by a combination of genetic factors and lifestyle choices. Obesity, a sedentary lifestyle, and poor dietary habits can all contribute to the development of insulin resistance. By identifying and addressing these causes, you can begin the journey towards reversing type 2 diabetes.
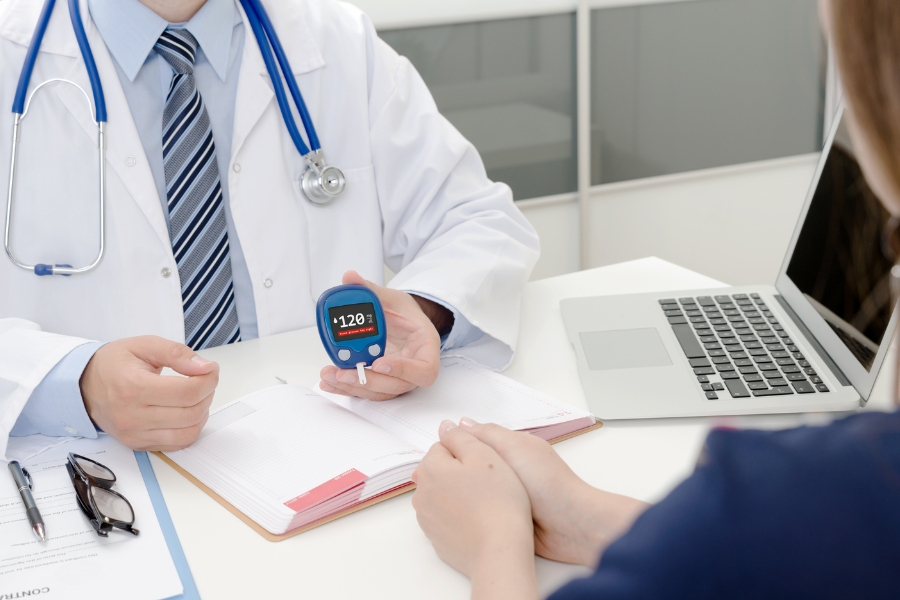

Understanding the Causes of Type 2 Diabetes
The Importance of Diet in Reversing Type 2 Diabetes
One of the most powerful tools in reversing type 2 diabetes is overhauling your diet. By making smart choices about the foods you consume, you can improve your blood sugar control and reduce insulin resistance. A diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is essential. These foods provide essential nutrients and are low in added sugars and unhealthy fats. Additionally, incorporating foods with a low glycemic index can help stabilize blood sugar levels. It is also important to limit your intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and foods high in saturated fats.
Overhauling Your Diet for Better Blood Sugar Control
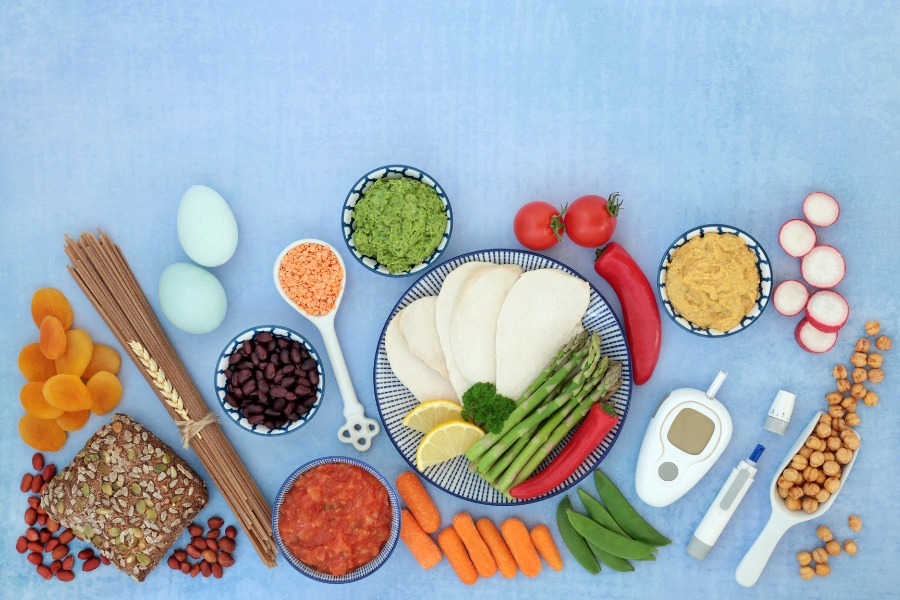

Overhauling Your Diet for Better Blood Sugar Control
While I can’t provide specific dietary advice, I can offer some general guidelines that may help support better blood sugar control:
Focus on whole, unprocessed foods:
- Vegetables: Aim for a variety of colorful vegetables at each meal. They’re packed with nutrients and low in calories and carbohydrates.
- Fruits: Choose whole fruits over juices, which lack fiber and can cause blood sugar spikes.
- Whole grains: Opt for brown rice, quinoa, whole-wheat bread, etc., over refined grains like white bread or pasta. They provide sustained energy and are rich in fiber.
- Lean protein: Sources like fish, chicken, beans, and lentils are low in saturated fat and can help manage blood sugar levels.
- Healthy fats: Include unsaturated fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. They promote satiety and offer various health benefits.
Limit certain foods:
- Added sugars: Reduce sugary drinks, processed foods, and sweets. These can cause blood sugar levels to spike and possibly lead to a stroke.
- Refined carbohydrates: Avoid white bread, pastries, and sugary cereals. They are quickly digested, leading to blood sugar fluctuations.
- Unhealthy fats: Limit saturated and trans fats found in fried foods, processed meats, and full-fat dairy products.
Additional tips:
- Eat regular meals and snacks: This helps maintain consistent blood sugar levels throughout the day.
- Control portion sizes: Pay attention to serving sizes to avoid overeating and blood sugar spikes.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to aid digestion and improve overall health.
- Consult a healthcare professional: For personalized guidance, consult a registered dietitian or doctor who can create a blood sugar-friendly meal plan specific to your needs and health conditions.
Remember: It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes, especially if you have any underlying health conditions. They can offer personalized advice and ensure your approach aligns with your specific needs and medical history.
The Role of Weight Loss in Reversing Type 2 Diabetes

The Role of Weight Loss in Reversing Type 2 Diabetes
While achieving complete reversal of type 2 diabetes remains a subject of ongoing research, weight loss has emerged as the most potent and well-established strategy in promoting remission, particularly when combined with other lifestyle changes.
How weight loss helps:
- Reduces fat in the pancreas and liver: Excess fat buildup in these organs can impair insulin function, leading to type 2 diabetes. Weight loss helps reduce this fat, improving insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
- Improves insulin sensitivity: Losing weight can make your cells more responsive to insulin, allowing them to absorb glucose more effectively from the bloodstream.
Weight loss recommendations for reversing type 2 diabetes:
- Aim for a weight loss of 5-10% of your body weight.
- Focus on sustainable lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet and regular physical activity.
- Consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support.
Additional factors to consider:
- While weight loss is crucial, it may not be the only factor for everyone. Some individuals may still require medication to manage their diabetes.
- The likelihood of achieving remission increases the sooner weight loss is initiated after diagnosis.
- Maintaining a healthy weight and lifestyle after achieving remission is essential to prevent the return of diabetes.
Remember, consulting with a healthcare professional is vital for creating a safe and effective weight loss plan that fits your individual needs and health condition.
Regular exercise plays an important role in reversing type 2 diabetes

Regular exercise plays an important role in reversing type 2 diabetes
While regular exercise is a crucial element in managing type 2 diabetes, it’s important to clarify that it’s not solely responsible for reversing the condition. Here’s a more nuanced perspective:
Significant benefits:
- Improved insulin sensitivity: Exercise helps your body utilize insulin more effectively, leading to better blood sugar control.
- Weight management: Regular physical activity can aid in weight loss, a crucial factor in managing type 2 diabetes.
- Overall health: Exercise offers numerous health benefits, including reducing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other complications associated with diabetes.
Reversal potential:
- Early stages: In some cases, particularly in the early stages of type 2 diabetes, intensive lifestyle interventions, including regular exercise and dietary changes, may lead to remission, meaning blood sugar levels can be maintained within normal range without medication.
- Combined approach: Reversing type 2 diabetes often requires a multi-faceted approach, including exercise, healthy diet, and potentially medication, depending on the severity of the condition.
Crucial points:
- Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have type 2 diabetes.
- They can help create a personalized plan considering your individual needs and health condition.
- While exercise plays a vital role, it’s crucial to manage type 2 diabetes holistically, potentially including medication and dietary adjustments.
Remember, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, balanced diet, and following your doctor’s guidance is key to effectively managing type 2 diabetes and improving your overall well-being.
Cut down on sugar and refined starches to reverse type 2 diabetes

Cut down on sugar and refined starches to reverse type 2 diabetes
Reducing your intake of sugar and refined starches can be a crucial step in managing type 2 diabetes, but it’s important to understand that it may not lead to complete reversal for everyone. Here’s a breakdown of the potential benefits and the importance of consulting a healthcare professional:
Potential benefits of reducing sugar and refined starches:
- Improved blood sugar control: By limiting refined carbohydrates and sugar, which break down quickly into glucose (blood sugar), you can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce blood sugar spikes.
- Reduced need for medication: In some cases, significant dietary changes, like reducing sugar and refined starches, can lead to needing less medication or even achieving medication-free diabetes management. However, this should be discussed and monitored by a doctor.
- Overall health benefits: Eating a healthy diet that’s lower in sugar and refined starches can also contribute to improved weight management, reduced risk of heart disease, and overall better health.
Why consulting a healthcare professional is crucial:
- Individualized guidance: Every person with type 2 diabetes has unique needs and circumstances. A doctor or registered dietitian can create a personalized plan that considers your specific health, medications, and lifestyle.
- Monitoring and adjustments: They can monitor your progress and adjust your plan as needed, ensuring you’re getting the nutrients you need while managing your blood sugar effectively.
- Addressing potential risks: While reducing sugar and refined starches is generally beneficial, it’s important to do so under the supervision of a healthcare professional to avoid potential risks, such as nutrient deficiencies or interactions with medications.
Remember, reversing type 2 diabetes is a complex process that often involves a combination of lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and medication. While reducing sugar and refined starches can be a significant step, it’s crucial to consult with a doctor or registered dietitian to develop a safe and effective plan for managing your type 2 diabetes.
Benefits of drinking enough water to control type 2 diabetes

Benefits of drinking enough water to control type 2 diabetes
While drinking enough water isn’t a cure for type 2 diabetes, staying hydrated offers several benefits that can significantly aid in managing the condition:
1. Helps regulate blood sugar: When you’re dehydrated, your body tries to conserve water by pulling it from your blood, leading to thicker blood and higher blood sugar levels. Drinking enough water helps thin the blood, making it easier for insulin to transport glucose into cells, which can help control blood sugar levels.
2. Supports kidney function: People with diabetes are at increased risk of kidney problems. Proper hydration helps the kidneys flush out excess glucose and waste products from the body, reducing the strain on the kidneys and potentially slowing their decline.
3. Prevents dehydration-related complications: Dehydration can worsen several diabetes-related complications, such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS), both of which can be life-threatening.
4. Aids in weight management: Staying hydrated can help you feel fuller for longer, potentially reducing calorie intake and aiding in weight management, which is beneficial for overall diabetes control.
5. Improves overall health: Adequate hydration is crucial for various bodily functions, including digestion, circulation, and nutrient absorption. Staying hydrated can improve your overall health and well-being, which is essential for managing diabetes effectively.
It’s important to note that the exact amount of water needed can vary depending on individual factors like age, activity level, and climate. However, it’s generally recommended to drink around eight glasses (2 liters) of water daily. Consulting a healthcare professional can help determine the optimal water intake for your specific needs.
Track your blood sugar and what it means for managing type 2 diabetes
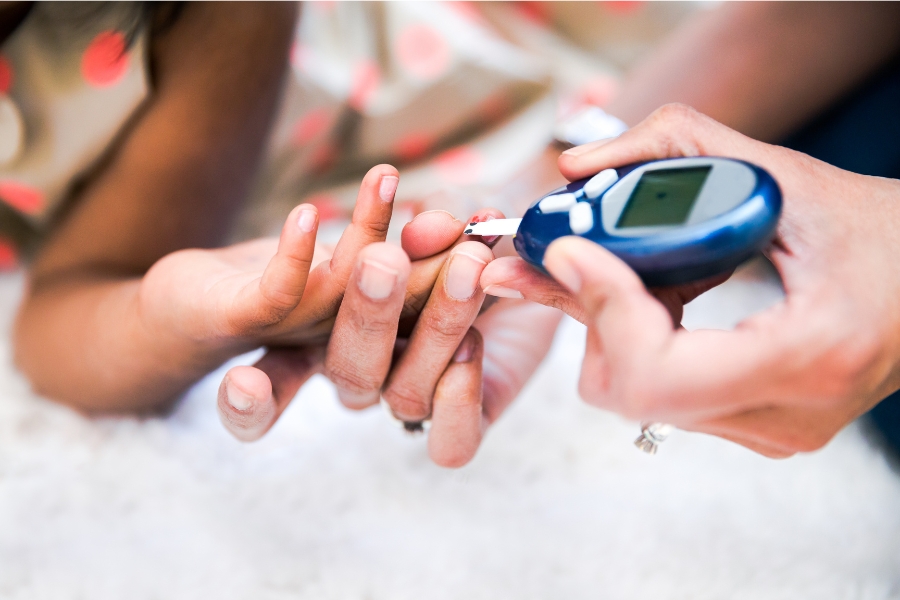
Track your blood sugar and what it means for managing type 2 diabetes
Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels is essential in managing type 2 diabetes. By tracking your blood sugar readings, you can identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to your diet and lifestyle. Work with your healthcare provider to set target blood sugar levels and determine the frequency of monitoring. Record your readings and share them with your healthcare team. This collaboration will help you make informed decisions about your diabetes management and ensure you are on the right track to reversing type 2 diabetes.
There are two main ways to track your blood sugar:
- Finger prick test: This is the traditional method of testing blood sugar. You will need a blood glucose meter, lancet device, and test strips. To test your blood sugar, you will first need to wash your hands. Then, you will use the lancet device to prick your finger and get a small drop of blood. You will then place the blood on a test strip and insert the strip into the meter. The meter will display your blood sugar level.
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): A CGM is a small sensor that is inserted under the skin. The sensor measures your blood sugar levels around the clock and sends the information to a receiver or a mobile app. CGMs can be more convenient than finger prick tests, as they can provide you with a more complete picture of your blood sugar levels.
How often you should test your blood sugar depends on several factors, including:
- Your type of diabetes
- Your blood sugar control goals
- Your treatment plan
Your doctor will recommend a blood sugar testing schedule that is right for you.
What your blood sugar numbers mean:
- Before a meal (fasting): Your blood sugar level should be between 80 and 130 mg/dL.
- Two hours after a meal: Your blood sugar level should be less than 180 mg/dL.
If your blood sugar levels are outside of these ranges, you should talk to your doctor.
Here are some tips for keeping track of your blood sugar:
- Keep a log of your blood sugar readings, including the date, time, your blood sugar level, and what you ate and drank before the test.
- Share your blood sugar log with your doctor at your regular appointments.
- Talk to your doctor about setting blood sugar goals for yourself.
By tracking your blood sugar and working with your doctor, you can help manage your type 2 diabetes and live a healthy life.
It is important to note that this information is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Consult your doctor before making any changes to your diabetes management plan.
The Role of Sleep in Managing Type 2 Diabetes

The Role of Sleep in Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Sleep plays a crucial role in managing type 2 diabetes, a chronic condition where the body struggles to regulate blood sugar levels. Here’s how getting enough quality sleep benefits those with type 2 diabetes:
1. Impact on Blood Sugar Control:
- Insulin sensitivity: Adequate sleep helps the body use insulin effectively, regulating blood sugar levels. Chronic sleep deprivation can decrease insulin sensitivity, leading to higher blood sugar levels.
- Hormonal regulation: During sleep, the body releases hormones like leptin (promotes satiety) and adiponectin (improves insulin sensitivity). Conversely, sleep deprivation increases ghrelin (increases appetite) and cortisol (raises blood sugar).
2. Potential Benefits of Good Sleep:
- Improved glycemic control: Studies suggest that getting 7-8 hours of sleep nightly can improve blood sugar control and reduce the need for medication.
- Reduced risk of complications: Adequate sleep may lower the risk of developing diabetes-related complications like heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
- Enhanced weight management: Good sleep can help regulate appetite and food choices, potentially aiding weight management, which is crucial for type 2 diabetes control.
3. Recommendations for Sleep Hygiene:
- Establish a regular sleep schedule: Go to bed and wake up at consistent times, even on weekends, to regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine: Wind down before bed with calming activities like reading, taking a warm bath, or listening to calming music.
- Optimize your sleep environment: Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, cool, and clutter-free to promote restful sleep.
- Limit screen time before bed: Blue light emitted from electronic devices can disrupt sleep. Limit screen time at least an hour before bed.
- Seek professional help if needed: If you experience sleep disturbances like sleep apnea or insomnia, consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
By prioritizing good sleep hygiene and aiming for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night, individuals with type 2 diabetes can contribute significantly to managing their condition and improving their overall health and well-being.
Reduce stress to naturally control and reverse type 2 diabetes

Reduce stress to naturally control and reverse type 2 diabetes
While research shows a strong correlation between stress and blood sugar levels, it’s important to understand that reducing stress alone cannot reverse type 2 diabetes. However, managing stress through healthy practices can be a valuable tool, alongside a doctor-supervised treatment plan, to help control your blood sugar levels and improve your overall well-being.
Here’s how reducing stress can be beneficial for managing type 2 diabetes:
- Stress hormones like cortisol can increase blood sugar levels. Chronically high stress levels can lead to the body producing more cortisol, which can impair insulin sensitivity and make it harder for your body to use insulin effectively.
- Stress can lead to unhealthy lifestyle choices. When stressed, people are more likely to engage in unhealthy coping mechanisms like overeating, smoking, or lack of physical activity, all of which can worsen blood sugar control.
- Stress can make it harder to manage diabetes self-care. The emotional toll of managing a chronic condition like diabetes can be stressful, and chronic stress can make it harder to stay motivated and consistent with healthy habits like following a meal plan, taking medications, and getting regular exercise.
Therefore, incorporating stress management techniques into your routine can be a valuable addition to your diabetes management plan. Here are some things you can try:
- Relaxation techniques: Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help activate the body’s relaxation response, lowering stress hormones and promoting feelings of calm.
- Mindfulness: Mindfulness practices like mindful meditation and spending time in nature can help you become more aware of your thoughts and feelings and cultivate a sense of acceptance and non-judgment.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity is a well-established way to reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Getting enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night. When you’re well-rested, you’re better equipped to handle stress.
- Healthy social connections: Spending time with loved ones and building strong social connections can provide emotional support and buffer the negative effects of stress.
- Seek professional help: If you’re struggling to manage stress on your own, consider seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor. They can teach you coping mechanisms and provide support for managing stress and improving your overall emotional well-being.
Remember, it’s crucial to consult with your doctor before making any significant changes to your diabetes management plan, including incorporating new stress management techniques. They can help you create a personalized plan that addresses your individual needs and medical conditions.
Food and herbal supplements to control and reverse type 2 diabetes

Food and herbal supplements to control and reverse type 2 diabetes
While there is no single food or herbal supplement that can definitively reverse type 2 diabetes, there are several options that can aid in managing blood sugar levels and potentially contribute to achieving remission when used alongside a doctor-recommended treatment plan that typically includes:
- Healthy eating: This focuses on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein while limiting processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.
- Regular exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Weight management: Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly improve blood sugar control.
- Medications: These may include oral medications or insulin, depending on the severity of your condition.
Here are some examples of foods and supplements that may be helpful when used under the guidance of a healthcare professional:
Foods:
- High-fiber foods: These help regulate blood sugar by slowing down digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. Examples include legumes, whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Healthy fats: Unsaturated fats, such as those found in olive oil, avocado, and nuts, can improve insulin sensitivity.
- Cinnamon: Studies suggest that cinnamon may help lower blood sugar levels. However, it’s important to use it in moderation as high doses can have side effects.
Supplements:
- Vitamin D: Deficiency in vitamin D has been linked to an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Supplementation may be beneficial, but consult your doctor first to check your levels and determine the appropriate dosage.
- Magnesium: This mineral plays a role in insulin function and blood sugar control. However, people with certain health conditions, such as kidney disease, should avoid magnesium supplements.
In addition to a healthy diet, certain food and herbal supplements may aid in diabetes management. However, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider before incorporating any supplements into your routine. Some supplements that have shown promise in managing blood sugar levels include cinnamon, chromium, alpha-lipoic acid, and berberine. These supplements may enhance insulin sensitivity or have other beneficial effects on blood sugar control. Remember that supplements should complement a healthy lifestyle and should not be relied upon as the sole treatment for type 2 diabetes.
The Benefits of Intermittent Fasting for Type 2 Diabetes

The Benefits of Intermittent Fasting for Type 2 Diabetes
Intermittent fasting (IF) has gained popularity as a potential approach for managing various health conditions, including type 2 diabetes. While research is ongoing, some studies suggest that IF may offer certain benefits for individuals with this condition.
Potential benefits of intermittent fasting for type 2 diabetes:
- Improved blood sugar control: IF may help regulate blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and reducing the body’s production of glucose. This can potentially lead to lower blood sugar levels and a reduced need for medication.
- Weight loss: Losing weight can significantly improve blood sugar control in individuals with type 2 diabetes. IF may promote weight loss by restricting the eating window and potentially reducing overall calorie intake.
- Reduced inflammation: Chronic inflammation is thought to play a role in the development and progression of type 2 diabetes. Some studies suggest that IF may help reduce inflammation in the body, which could potentially benefit individuals with this condition.
It is important to note that:
- IF is not a guaranteed approach for everyone with type 2 diabetes. Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial before starting any new dietary or lifestyle changes, including IF.
- IF may interact with certain medications. Individuals taking medications for type 2 diabetes should closely monitor their blood sugar levels and consult with their doctor before attempting IF.
- IF may not be suitable for everyone. It is essential to listen to your body and discontinue IF if you experience any negative side effects.
Additional considerations:
- There are different types of IF protocols. Some common approaches include the 16/8 method (fasting for 16 hours and eating within an 8-hour window), the 5:2 method (eating normally for 5 days and restricting calories on 2 non-consecutive days), and alternate-day fasting (fasting every other day).
- A healthy diet is still essential during eating periods. It is crucial to focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods during your eating window to ensure you are getting the nutrients your body needs.
- Staying hydrated is essential during fasting periods. Drink plenty of water, unsweetened tea, and black coffee to stay hydrated throughout your fast.
If you are considering trying intermittent fasting for type 2 diabetes, it is crucial to consult with your doctor or a registered dietitian to determine if it is safe and appropriate for you. They can help you create a safe and effective IF plan that meets your individual needs and goals.
Intermittent fasting has gained popularity as a strategy for managing and reversing type 2 diabetes. This eating pattern includes periods of intermittent fasting and alternating eating periods.. During fasting periods, the body can use stored glucose for energy, helping to lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. There are different fasting methods to choose from, such as the 16/8 method or alternate-day fasting. However, it is important to work with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate fasting protocol for your specific needs and medical condition.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Type 2 Diabetes Naturally
Reversing type 2 diabetes naturally is possible with dedication and lifestyle changes. By overhauling your diet, losing weight, exercising regularly, cutting down on sugar and refined starches, staying hydrated, monitoring your blood sugar levels, getting enough sleep, reducing stress, exploring food and herbal supplements, and trying intermittent fasting, you can take control of your type 2 diabetes and improve your overall health. Remember to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan that suits your specific needs. Together, you can reverse type 2 diabetes and enjoy a healthier, more fulfilling life.
CTA: Take the first step towards reversing type 2 diabetes naturally by consulting with your healthcare provider and creating a personalized plan tailored to your needs. With dedication and these 10 strategies, you can regain control of your health and live a life free from the burden of type 2 diabetes. Start your journey today!
















[…] Hyperglycemia is the result of a combination of factors that can disrupt the balance of glucose in my blood. One of the most common causes is diabetes, where my body either does not produce enough insulin (type 1 diabetes) or becomes resistant to insulin’s effects (type 2 diabetes). […]
[…] someone who manages diabetes, monitoring blood glucose levels is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. […]
[…] someone who has been living with diabetes for several years now, I understand the importance of making smart and nutritious choices when it […]